Searching¶
Introduction¶
The Internet contains an unbelievable amount of information, which is really not all that useful unless you can find what you’re looking for. After all, it’s not the volume of information that’s so powerful, it’s that somewhere within that enormous haystack is the needle you’ve been looking for. Search engines are all about finding the needle.Internet searching is one of the easiest and useful ways to use the Internet. There are endless reasons for why Internet searching is so helpful. People use common search engines (such as Google and Yahoo) to find web pages, images, books, currency conversions, definitions, file types, news, local information, movies, and many more. The most-used and best-loved search engine, by far, is Google. Built upon the philosophy, “Do no evil”, Google is useful, uncluttered, incredibly fast, remarkably on target, and really reliable. Many people believe that Google can only be used for inputing key words to web pages and getting results that share those key words. However, you can use Google to find so much more information and find it much more easily using specific built-in Google commands.
Google Interface¶
Of Note | The following information is for those of you out there looking for a basic introduction into common Google capabilities. Scroll down to the 6 Things You Might Not Have Known section for a more in depth look at the advanced capabilities of Google |
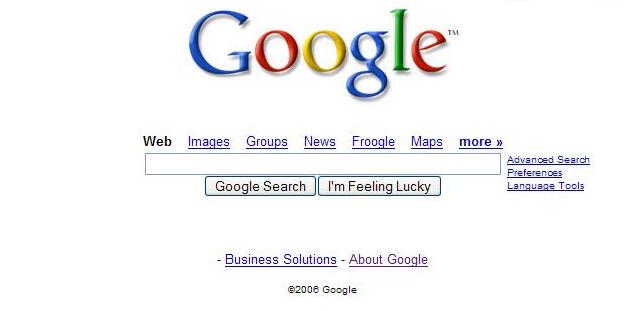
Out of all the features Google has theses days their number one capability is still their website searching. Google is so special because it is so simple. Google’s main page (below) is based around the search bar where users enter a query using keywords.
5 Basic Things To Know About Google¶
Query¶
A query consists of one or more words, numbers, or phrases that you want to find in the search results listings.
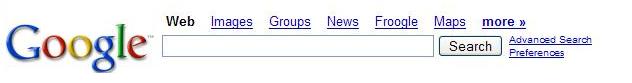
To enter a query, type descriptive words(keywords) into Google’s search box. You can use either the search box on Google’s home page (shown above) or the search box that always appears at the top of a Google results page (shown below).
Results¶
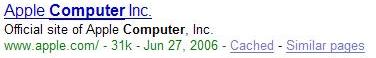
The results page is full of information and links, most of which relate to your query. Results Google considers to be most relevant to your query are shown first. To the right of Google’s search results appear sponsored links, which are paid advertisements.
The first line in each result is the page title. The title will be a link to the web page. Under the title are often excerpts which include one or more of your query words shown in boldface. The URL of the page is shown in green at the start of the last line under the result.
Cached Pages¶
To the right of the URL there is a link named “Cached”. The Cached link will take you to a screen shot of the page that Google took when it first found it. A lot of the content and images under the cached page may have been changed since websites are constantly updated.
Similar Pages¶
The Similar Pages*(To the right of the *Cached page) link will take you to a results page similar to the normal results page, but will have results similar to the result you linked from.
Keywords¶
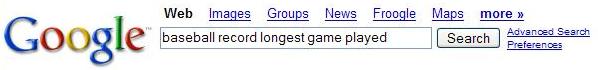
How do you know what keywords to enter into the search bar? Not only does it matter what words you enter, but the order you enter them will vary your results. A good rule for the order of words to have in your search is that the first word should be a word that if you only included that word, the results would be closest to what you wanted. Then the second word would be the word that if you included after the first word, the results would be the closest to what you were looking for. And so on and so on with the rest of the words you want to enter. For example, let’s say you wanted to search for information on the record for longest baseball game played. The first word you would want to enter is “baseball”, because if you only included “baseball” in your search, the results would be the closest to the record for the longest baseball game played. The second word would be “record” because with the phrase “baseball record” you would get results, such as a website containing a list of baseball records. However, if you had put “longest” second, then you probably would get results relating to longest home run or longest bat. Once you get to the third word the order does not matter that much, so you could follow “baseball record” with “longest game played”, “game longest played”, or “longest played game”, etc.
6 Things About Google You Might Not Have Known¶
There are many characters that you can use to affect the way Google uses the keywords you enter. Some of these helpful hints you might not have known.
Quotes¶
To search for a phrase, a proper name, or a set of words in a specific order, put them in double quotes. For example, say you wanted to search for the quoted phrase “to be or not to be” you would enter into Google [“to be or not to be”] (without the brackets).
Plus Sign¶
Force Google to include a term by preceding the term with a “+” sign. For example, if you wanted to search for Star Wars Episode 1. “I” is a stop word and is not included in a search unless you precede it with a + sign. So you would input into Google [Star Wars Episode +I] or [Star Wars +I]. Precede each term you do not want to appear in any result with a “-” sign.
Synonyms¶
Find synonyms by preceding the term with a ~, which is known as the tilde or synonym operator. Specify synonyms or alternative forms with an uppercase OR or | (vertical bar). Specify that results contain numbers in a range by specifying two numbers, separated by two periods, with no spaces.
Googlefight¶
If you aren’t sure what words you should use and in what order, try Googlefight. Googlefight allows you to compare the number of search results you would get for any two sets of keywords.
Having Favorites¶
Google favors results that have your search terms near each other. Google gives higher priority to pages that have the terms in the same order as in your query. Google also limits queries to 32 words.
Of Note | Google is NOT case sensitive; it shows both upper- and lowercase results. |
Stop Words¶
Google ignores some common words called “stop words,” (such as, the, on, where, how, and, de, la, as well as certain single digits and single letters along with some punctuation and special characters, including ! ? , . ; [ ] @ / # < >). A term with an apostrophe (single quotes) doesn’t match the term without an apostrophe.Because some people spell hyphenated words with a hyphen and others with a space, Google searches for variations on any hyphenated terms.
Advanced Web page Search¶
Google has created an “advanced”(Don’t be afraid!! This does not mean difficult) way to search for web pages by inputing detailed options that you want Google to keep in mind while it searches through web pages. Advanced Search
- The Find Results section allows you to narrow down results by changing the way Google uses the keywords you enter. You can have it search for pages containing: all, exact phrases, at least one, or none of the keywords you enter.
- The Language option allows you to make Google search for pages written in certain languages.
- The File Format option will give you results that are certain types of files, such as PDF’s, word documents, excel projects, etc.
- The Date option will give you web pages that have updated within the certain amount of time you select. Google gives you the option to choose among anytime, 3 months, 6 months, or one year.
- The Numeric Range option tells Google to search for pages containing numbers within the range you provide.
- The Occurrences option will provide you pages that show the keywords you provide in select locations on the page. It lets you choose among anywhere, the title, the text, the URL, or the links.
- The Domain option lets you search for web pages from a certain domain or pages not from a certain domain.
- The Usage Rights option lets you search for pages with certain types of usage rights. This is very important since most web pages have copyrights on the information on their pages and if you accidentally copy that information and put it in your own work, you can get in deep trouble.
- The ‘Safe Search option tells Google to either filter the results or not filter them.
- The Page-Specific Section lets you choose to search for pages that are related to a certain page, or pages that are linked to a certain page.
Images¶
A really handy feature of Google search is search for images. Searching for images is the second most used Google feature behind searching for web pages. There are multiple ways that Google allows you to search for images.
- Entering the words “clip art” or “gif” after your image request will yield the graphic version of the image, which is very usable in PowerPoint presentations and on web pages. However, using that method will provide you with a list of web pages containing images with names involving the keyword y ou entered For Example, the picture below shows a search for the keyword “bu ll gif” and the results are a list of web pages containing names of .gif files with the word “bull” in them:
- The concept of including the type of file you are searching for can be used with the keywords “bull gif” under the image search engine. This allows you to specify what type of image you are looking for:
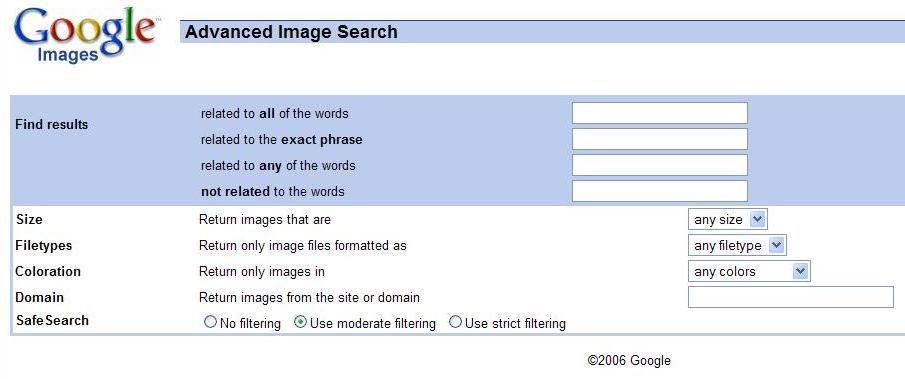
Advanced Image Search¶
Google has created the “Advanced Search” which allows you to narrow you’re results down to specifically what you’re looking for. The advanced search for images is accessed by clicking on the “Images” link to the right of the “Web” link on the main Google page. Once in the images section, there are two links, to the right of the search bar, which say “Advanced Image Search” and “Preferences”. Clicking on the “Advanced Image Search” takes you to a form which allows you to input specific information you want your resulting images to contain.
- The Find Results section is all about how you want your keywords entered
to relate to the resulting images.
- The related to all of the words line allows you to input a set of keywords which will generate results of images that relate to ALL of the keywords. For example, using the keywords ncaa basketball for this line and clicking Google Search will come up with results that relate to the wh ole phrase ncaa basketball.
- The related to the exact phrase line allows you to search for results that actually CONTAIN the words you input. For example, inputing the same phrase (ncaa basketball) will generate images that have the exact phrase ncaa basketball in the title of the image(such as,”ncaa_basketball_gam e.jpg”).
- The related to any of the words line allows you to have your results relate to ANY of the keywords you input. Following the same example, if yo u entered ncaa basketball to this line you would get images that relate to ncaa and then images that relate to basketball.
- The not related to the words line allows you to have your results NOT relate to ALL of the keywords you enter. In the example, inputing ncaa basketball will generate image results that do not relate to ncaa basketball. This line is recommended only with additional information in one of the above lines, since the results will have an incredibly large am ount of images and a vast variety of images if you only tell it NOT to sea rch for a specified keyword.
- The Size section allows you to narrow your image search to different image sizes. Google categorizes the sizes into small, medium, and large. Small pictures are usually as small as a 5x5 and as big as a 50x50 (as far as area goes). Mediums range from about 50x50 to 500x500. Larges are 500x500 and up.
- The Filetypes section allows you to narrow your image search to a specific type of image. This is useful since some programs/websites only allow you to use specific types of images. The file type options are JPG, GI F,and PNG.
- The Coloration section allows you to narrow your image search to a specific scale of colors that the image will contain. Google allows you to pick among any colors, black and white, gray scale, and full color images.
- The Domain section allows you to narrow your image search to a certain website where the images come from. This is helpful for specific websites which you know of having especially good images, or if you remember the name of a website where you saw a specific image, but you don’t remember exactly t he name of it.
- The Safe Search section allows you to filter your image search with either no filter, a moderate filter, or a strict filter.